|
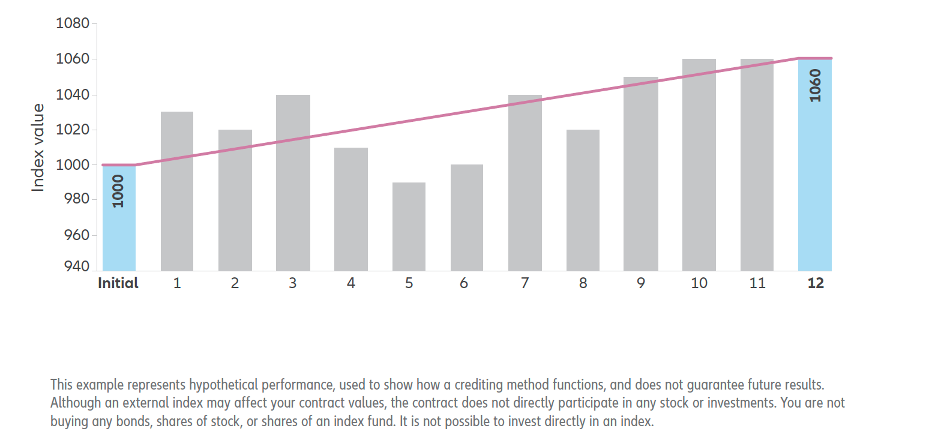
Fixed index annuities (FIAs) have many strong advantages to help protect your client’s savings and provide sustainable income over many years. Our goal is to help you gain a better understanding of the components that make up FIAs. This knowledge will enable you to make well informed decisions when it comes to product selection and design. FIAs accrue interest based on an external index, the index selected determines the amount of indexed interest received, which will fluctuate based on index change over the crediting period. The choice of the external index stands paramount. It is critical to explore the array of index options aligned with your FIA considerations. Equally crucial is the selection of the interest-crediting method for your FIA. The crediting method determines how fluctuations in the index will be calculated then credited to the annuity. The method chosen incorporates elements such as caps, spreads, and participation rates, which may greatly impact of indexed interest earned. In the subsequent sections, we delve into prevalent crediting methods, shedding light on how they work. Annual Point-to-PointA straightforward crediting methodology, annual point-to-point hinges on comparing the index value at two distinct points in time. This option could work well during periods of higher than usual mid-year volatility. Process Overview:
Illustrative Example: In a hypothetical scenario, if the ending index value surpasses the initial value by 6%, the indexed interest for the policy year could be contingent upon factors like a participation rate of 110%. Thus, the indexed interest would amount to 6.6%. However, if a cap is in place and is lower than the 6% increment, the indexed interest would be capped accordingly. Similarly, if a hypothetical scenario features a 3% spread, the indexed interest would be 3% (6% change in index value – 3% spread). Multi-Year Point-to-PointEchoing the principles of annual point-to-point, the multi-year point to point spans multiple years, thereby diminishing the influence of market volatility between the selected points. Process Overview:
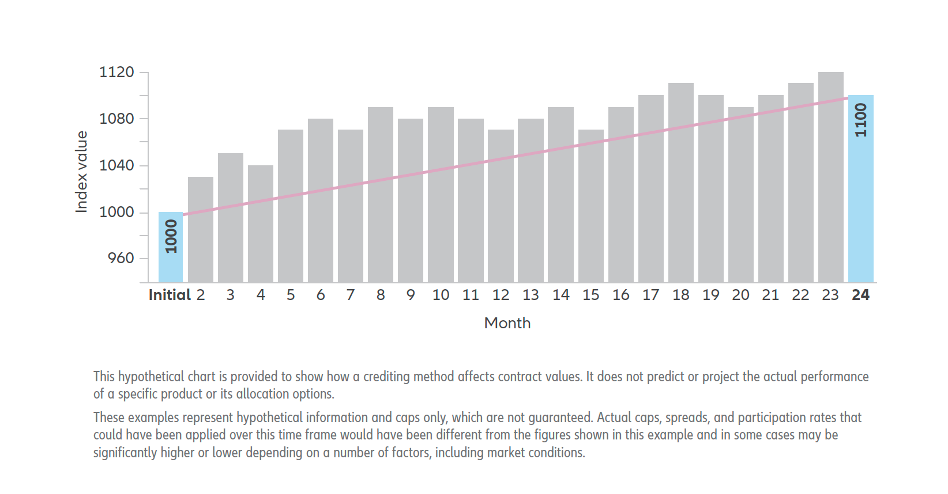
Illustrative Example: Consider a two-year point-to-point crediting scenario, where the ending index value outstrips the initial value by 10%. Assuming a participation rate of 150%, the indexed interest over the two contract years would amount to 15%. Monthly Sum This volatility-sensitive methodology tracks monthly index fluctuations, offering interest in buoyant markets while being susceptible to downturns. Process Overview:
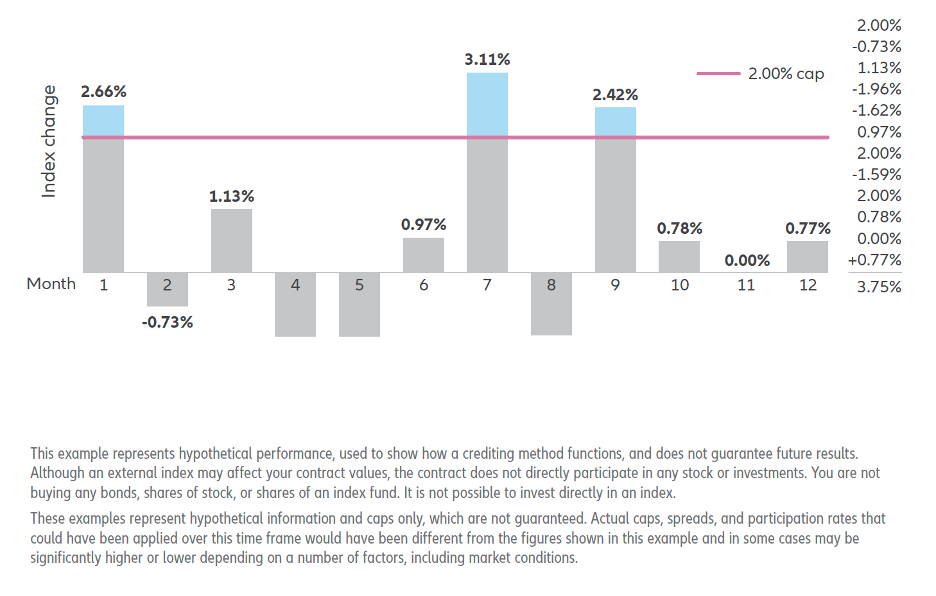
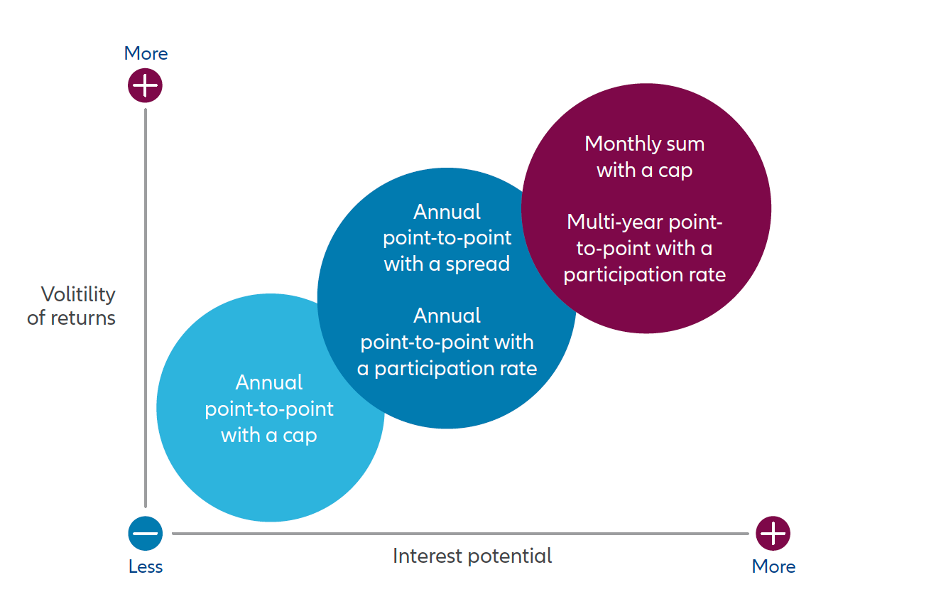
Illustrative Example: In a hypothetical monthly sum scenario with a 2.00% cap, monthly index fluctuations are evaluated. The cumulative sum determines the indexed interest, with any negative sum resulting in no interest accrual. FIA Crediting Methods: A Quick Overview Below is a chart outlining the relative sensitivity to performance volatility and interest potential of a few common Fixed Index Annuity (FIA) crediting methods.
Please note that this chart serves as a brief summary; it's essential to review the detailed descriptions of each crediting method before making a decision. Remember, no single method is universally superior. Depending on market conditions, one method may yield more interest than others—or no interest in a given year. Additionally, you have the option to combine crediting methods. Regardless of your choice, your accumulation value is safeguarded from negative performance.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
Categories |
Search Our Website to Find More Info, Tips, and Sales IdeasContact InformationOffice Address:
11611 N. Meridian Street | Ste 110 | Carmel, IN 46032 Phone: 1-877-844-0900 Fax: 317-844-4422 |
Quick Links |
THIS WEBSITE IS INTENDED FOR AGENT USE ONLY. NOT FOR USE BY CONSUMERS.
INFORMATION CONCERNING COPYRIGHT INFRINGEMENT CLAIMS
The Ohlson Group, Inc. provides links from its website to various third party sites which may enable you to obtain locations and information outside of The Ohlson Group's control. The Ohlson Group, Inc. neither controls nor endorses such other websites, nor have we reviewed or approved any content appearing on them. The Ohlson Group, Inc. does not assume any responsibility or liability for any materials available at these websites, or for the completeness, availability, accuracy, legality or decency of these sites.
CLAIMS OF COPYRIGHT INFRINGEMENT
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act of 1998, as amended, (the "DMCA") provides recourse for copyright owners who believe that material appearing on the Internet infringes their rights under U.S. copyright law. If you believe in good faith that materials we host infringe your copyright, you (or your agent) may send us a notice requesting that we remove the material or block access to it. If you believe in good faith that someone has wrongly filed a notice of copyright infringement against you, the DMCA permits you to send us a counter-notice. Notices and counter-notices must meet the then-current statutory requirements imposed by the DMCA; see http://www.loc.gov/copyright/ for details. Notices and counter-notices should be sent to [email protected]. The Ohlson Group, Inc., (877) 844-0900. We suggest that you consult your legal advisor before filing a notice or counter-notice. Also, please be aware that there are penalties for false claims under the DMCA.
The Ohlson Group Inc, and or Joseph R. Ohlson LUTCF is licensed to do business in all states except New York.
Privacy Policy
INFORMATION CONCERNING COPYRIGHT INFRINGEMENT CLAIMS
The Ohlson Group, Inc. provides links from its website to various third party sites which may enable you to obtain locations and information outside of The Ohlson Group's control. The Ohlson Group, Inc. neither controls nor endorses such other websites, nor have we reviewed or approved any content appearing on them. The Ohlson Group, Inc. does not assume any responsibility or liability for any materials available at these websites, or for the completeness, availability, accuracy, legality or decency of these sites.
CLAIMS OF COPYRIGHT INFRINGEMENT
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act of 1998, as amended, (the "DMCA") provides recourse for copyright owners who believe that material appearing on the Internet infringes their rights under U.S. copyright law. If you believe in good faith that materials we host infringe your copyright, you (or your agent) may send us a notice requesting that we remove the material or block access to it. If you believe in good faith that someone has wrongly filed a notice of copyright infringement against you, the DMCA permits you to send us a counter-notice. Notices and counter-notices must meet the then-current statutory requirements imposed by the DMCA; see http://www.loc.gov/copyright/ for details. Notices and counter-notices should be sent to [email protected]. The Ohlson Group, Inc., (877) 844-0900. We suggest that you consult your legal advisor before filing a notice or counter-notice. Also, please be aware that there are penalties for false claims under the DMCA.
The Ohlson Group Inc, and or Joseph R. Ohlson LUTCF is licensed to do business in all states except New York.
Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 The Ohlson Group, Inc. All Right Reserved.



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed